INSTALLATION AND SET UP OF SYS-INTERNALS TOOL
WHAT IS A SYSINTERNALS TOOL?
The SysInternals suite of tools is simply a set of Windows applications that can be downloaded for free from Microsoft tech website. They are used as tools to generate red flags for figuring out possibility of malware in a system and to properly remove such malware, securely and completely from your system. It is one of the important incident response tools for Window users.
INSTALLATION OF SYINTERNALS SUITE :
- Click on https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/sysinternals/downloads/sysinternals-suite to download lattest version of Sysinternal suite.
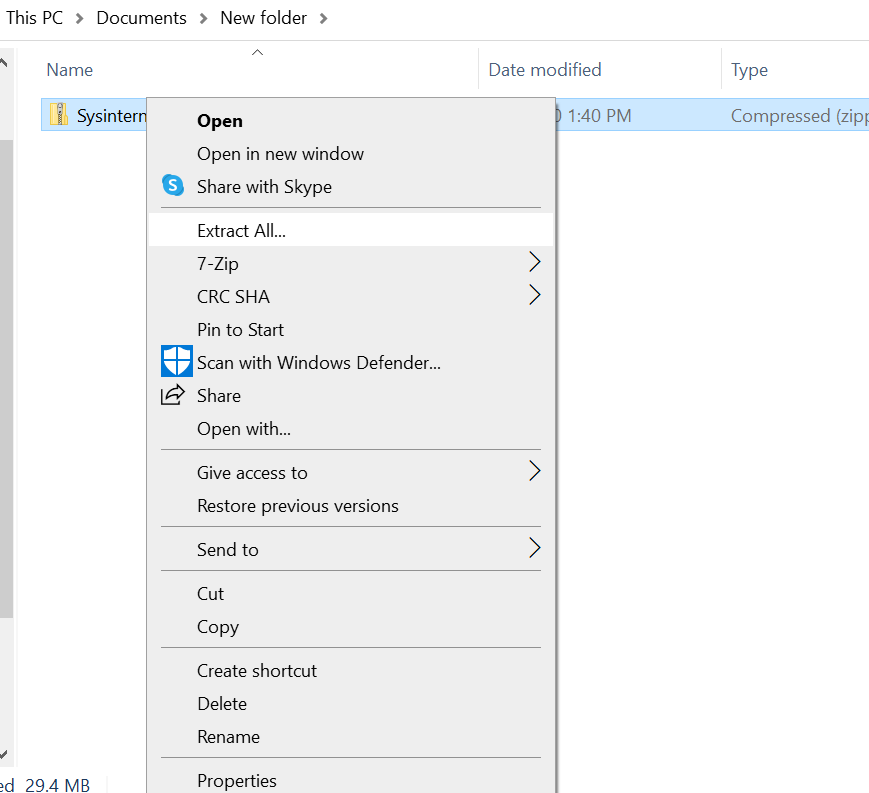
2. Unzip the file by right clicking on the file you just downloaded and select Extract All :
3. A list of tools appears as below :
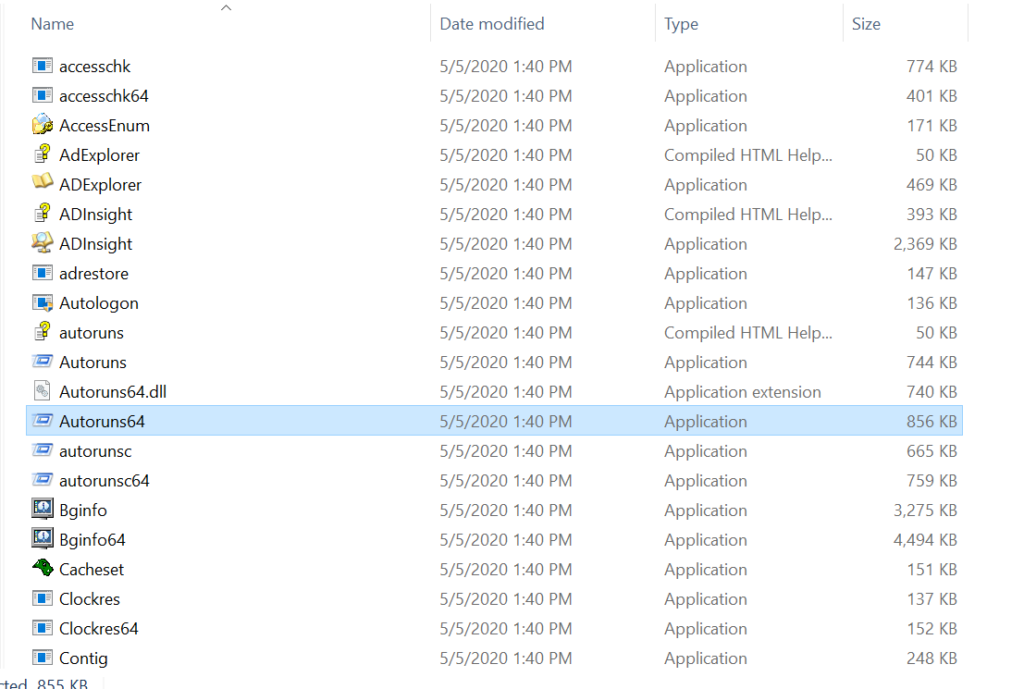
4. Focus on 3 Important tools from the list, which are Autoruns ( for 32 bit windows) , Autoruns64 ( for 64 bit windows), procexp (for 32 bit windows), procexp64 (for 64 bit windows) and Tcpview.
AutoRuns
Autoruns feature is useful in analyzing the processes which can auto start itself in the user system i.e without user’s permission.
By considering the possible red flags generated by a selected program, one can decide to see if that program should be running or should be disabled from the system to reduce further damage.
Make sure you run the tool with “run as administrator” privileges as below :
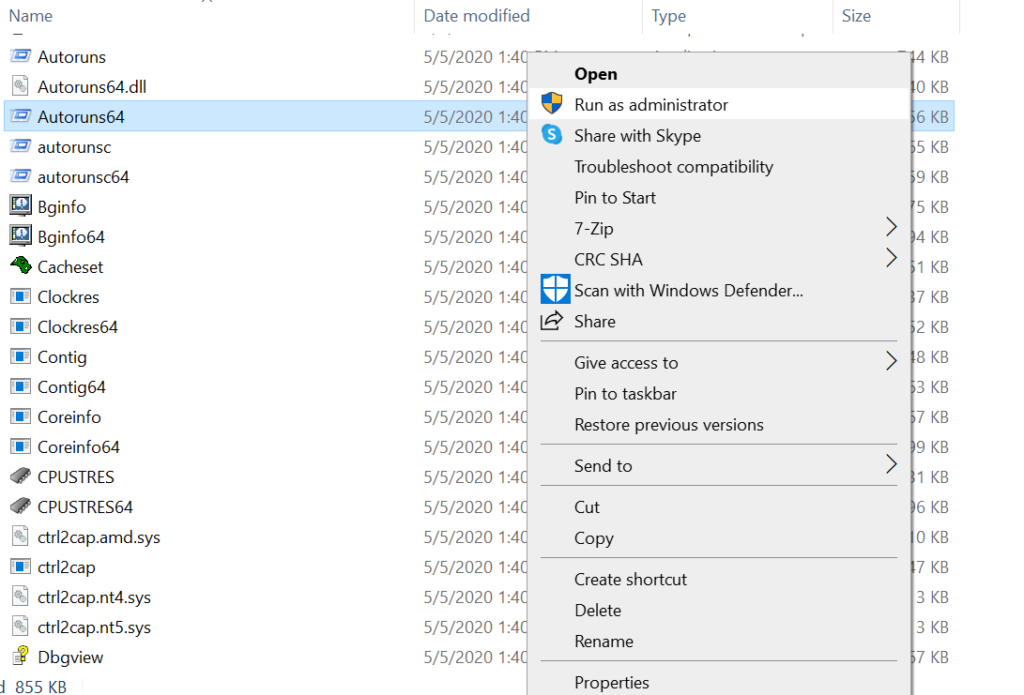
By considering the possible red flags generated by a selected program, one can decide to see if that program should be running or should be disabled from the system to reduce further damage.
Red flags include :
- To check for apps/programs unknown to you by their description and icons.
- To check if the app/file icon is generic or not. Most genuine files/apps consist of their brand symbol instead of generic ones.
- To check if files contain proper description with verified publishers.
- To check for malware suggestions by virustotal.
- To check the timestamp for some clue for when the app was created or modified.
Jump to entry : Opens the location where the autostart entry is configured. It starts the registry editor (Regedit.exe) and sends it simulated keystrokes to navigate to the autostart entry.
Jump to image : Opens a new Windows Explorer folder window with the file identified as the target image selected.
Check for virus total : It checks for any possible malware detection related to a particular file or application with the help of suggestions by more than 65+ reputed antivirus softwares.
Search Online : It searches for the information or description of a particular file or application selected from the web.
Properties : Gives information about the date of access, creation and modification of the file/application. It also provides the size and location of the file/application.
After selecting the “Jump to image” option for a particular program/app, one can track the exact location of the file. Most of these files usually end up in the C drive. One can decide whether to delete it or not.
Major importance needed to give on autorun processes are to check for red flags or say symptoms for possible malware.
One can also go to options and select “scan options” in autoruns. Then tick on the check virustotal.com to submit file hash and get the feedback from virustotal regarding all the files.
One can also go to options in autoruns and hide microsoft entries so as to reduce the list of verified microsoft genuine apps which doesn’t require to monitor again and again.
Malwares can be identified by searching it online through uses of CLSID (Class Identifier which is a serial number that represents a unique ID for any application component in Windows.
One good option to search for certain file information is to go to the website
( systemlookup.com ). One can copy the file name and paste it on the search bar of the website to see the background history and other information regarding the file.
Process Explorer
Process explorer is similar to windows task manager in its functionality but also adds many more features to collect information about processes running in your user system.
Make sure you run the tool with Administrator privileges:
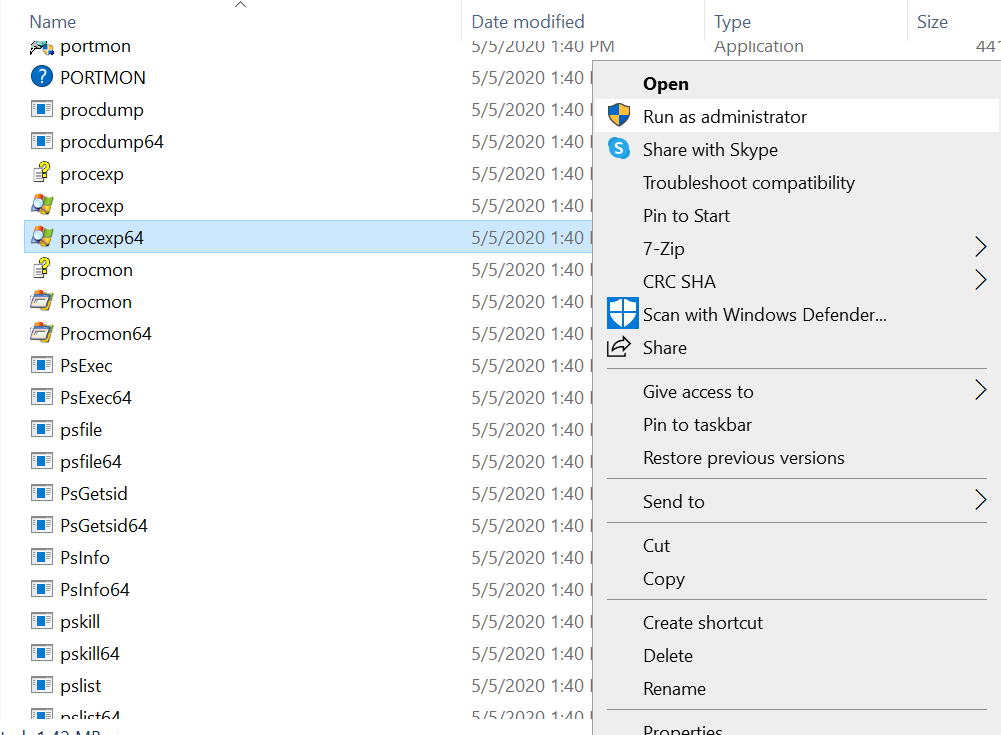
Selecting a file and clicking the right mouse button will result in a pop up showing options such as : set affinity, set priority, kill process, kill process tree, restart, suspend, create dump and properties.
- Set affinity : Provides the user to set how many CPU cores to be used for the particular file or application being selected.
- Set priority : Provides the user to set how much CPU power consumption to be allowed for a particular file or application.
- Kill process : Kills the particular process being selected which is running on the system.
- Kill process tree : Kills the particular process with its parent processes associated with it.
- Restart : Restarts the file or application being selected.
- Suspend : It temporarily suspends or pauses the selected app from being able to process in the system.
- Create dump : It stores the data stored by a program in its ram so that later through that information, one can research for what may have gone wrong in the program or for any possible malware activities.
- Properties : Can check file properties such as image file path, storage, Cpu usage, list of strings used in it and etc.
- Search Online : Searches for information related to the selected file from the web.
One can go to the options menu and tick on verify image signatures to get a clue whether files or programs have verified signatures from their brand.
One can also tick on the virustotal option to see for any suggestions for a possible malware from all the antiviruses listed in virustotal.
TCP view
It is used to monitor network traffic to troubleshoot any issues in the computer network. It gives real time information about which ports are currently established, which ports are closed and which ones are currently listening. It gives information about how many data is being sent by a program and how many are received through various ports.
Running the tool with administrator privileges :
The TCP view output looks like below :
As every program needs to communicate at some point of the time for updates or real time web access, red flags for possible malware behavior in TCP view could be judged from
- How many datas are being sent to a remote server through the column under “SENT BYTES”. If a certain app for example “adobe illustrator” is sending suspicious amounts of data to an external server (which is generally not expected) a red flag is generated
- Who they are communicating with by checking the ip address under the column section of “Remote Address”.
Options for Tcp view are :
- “Process properties” which gives information about the path and version of the process.
- “End process” is a direct option for the user to end the process being selected.
- “Close connection” provides the user to close a particular port from being connected to a network to which it has been connecting before.
- “Who is” option gives information about a particular port from the web.
DISCLAIMER
- Before launching autoruns, process explorer and Tcp view, it is important to note that it should be run as administrator. This gives you administrative privileges to monitor and modify your programs in the sysinternal suite.
- All apps and programs which don’t consist of verified signatures should not be categorized as possible malwares. This is because getting verified signatures is an expensive process and thus some genuine apps don’t have verified signatures to avoid spending money on it.

0 Comments