Don’t wait for Update
Updating your computer software is the easiest way to block online attacks.
Everyone has received notices on their computers saying “Software Update Available: Update Now or Remind Me Later”. Choosing “Update Now” is simple and powerful way to stay safer online.
What is software update?
All software programs – including your computer’s operating system like Windows or Mac – have security vulnerabilities in them that are discovered over time. Attackers can take advantage of these weaknesses to get easy access to your computer. A software update, which is sometimes called a software patch, is a free download for an application, operating system, or software suite that provides fixes for features that aren’t working as intended or adds minor software enhancements and compatibility. Software updates are released to address security issues when they occur, to address minor bugs discovered in the software, to improve the operation of hardware or peripherals, and to add support for new models of equipment. These small, incremental updates improve the operation of your software.
A common operating system update is a security update, which is issued to protect your computer against vulnerabilities that might be exploited by hackers and malware.
Why Software Update is Important?
Although they are typically small and free, software updates play important roles often related to solving or preventing a problem:
- Protect against new-found security risks
- Introduce new features in your software
- Improve battery depletion rate or performance speed
- Extend your equipment’s usable life by allowing its maximum productivity
- Fix bugs in the software and improve functionality
How to Update?
Windows prompts users to update every week on its own. But in case this doesn’t happen, you can manually look for updates. To do so, go to Settings and then click on Update and Security.
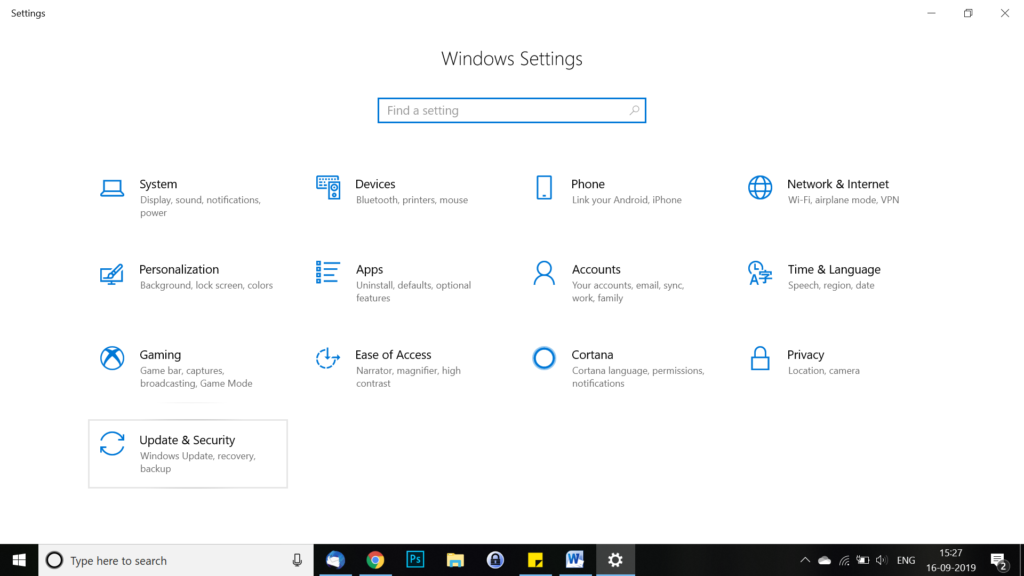
click on “Windows Update”. Check for updates and if you see ‘Updates are available’ then you can click on ‘Restart now’ if you want to update right away or you can schedule for later.
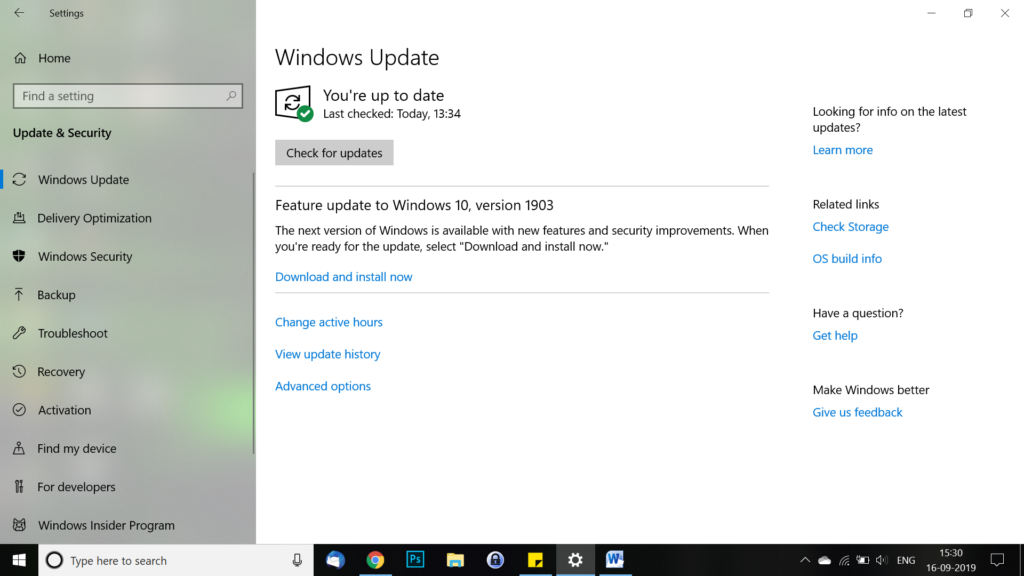
How to get updates for macOS Mojave or Catalina(Which will be releasing in fall)
If you have upgraded to macOS Mojave, follow these steps to keep it up to date:
- Choose System Preferences from the Apple menu , then click Software Update to check for updates.
- If any updates are available, click the Update Now button to install them. Or click ”More info” to see details about each update and select specific updates to install.
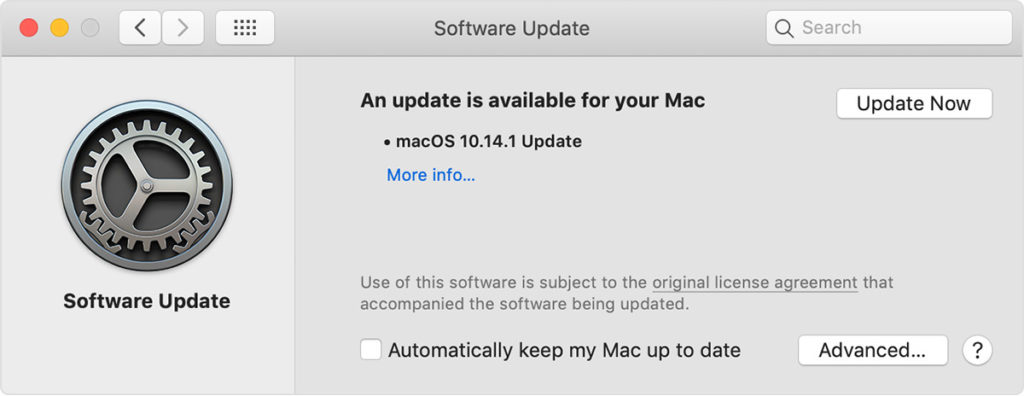
3. When Software Update says that your Mac is up to date, macOS and all of its apps are also up to date. That includes Safari, iTunes, Books, Messages, Mail, Calendar, Photos, and FaceTime.
To find updates for iMovie, Garageband, Pages, Numbers, Keynote, and other apps that were downloaded separately from the App Store, open the App Store on your Mac, then click the Updates tab.
To automatically install macOS updates in the future, including apps that were downloaded separately from the App Store, select ”Automatically keep my Mac up to date.” Your Mac will notify you when updates require it to restart, so you can always choose to install those later.
How to get updates for earlier macOS versions
If you’re using an earlier macOS, such as macOS High Sierra, Sierra, El Capitan, or earlier,* follow these steps to keep it up to date:
- Open the App Store app on your Mac.
- Click Updates in the App Store toolbar.
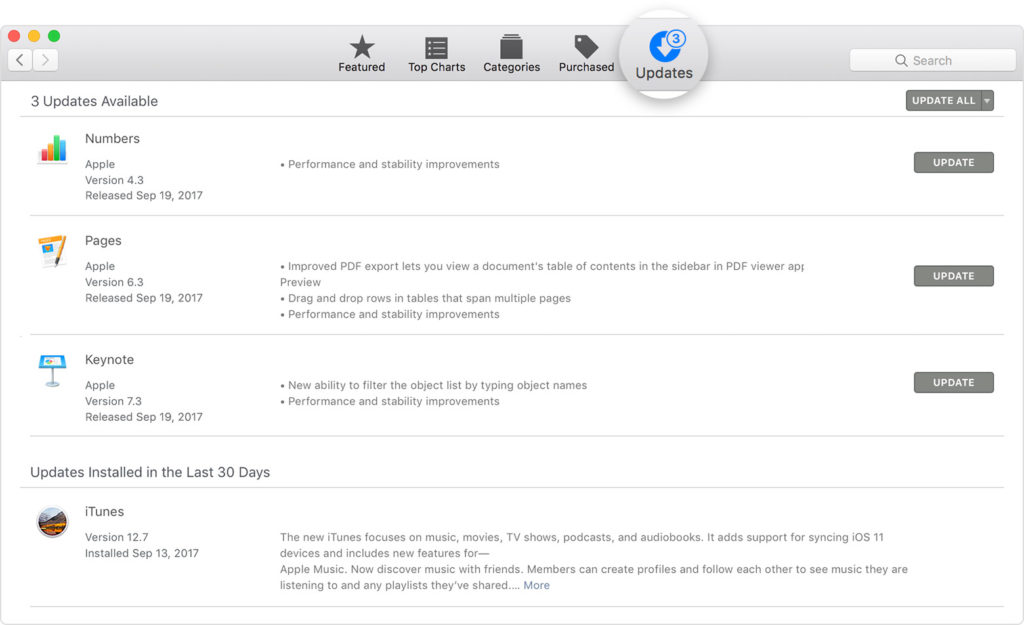
Use the Update buttons to download and install any updates listed.
3. When the App Store shows no more updates, your version of macOS and all of its apps are up to date.
4. That includes Safari, iTunes, iBooks, Messages, Mail, Calendar, Photos, and FaceTime. Later versions may be available by upgrading your macOS.
To automatically download updates in the future, choose Apple menu > System Preferences, click App Store, then select ”Download newly available updates in the background.” Your Mac will notify you when updates are ready to install.
How to update Linux (Ubuntu)
Ubuntu Linux has become one of the most popular of all the Linux distributions. And through the process of updating a system, you should be able to tell exactly why this is the case. Ubuntu is very user friendly. Ubuntu uses two different tools for system update:
Method 1 : Update Ubuntu via Command line tool.
*Note: This tutorial is valid for Ubuntu 18.04, 16.04, or any other version. The command line method is also valid for Ubuntu-based Linux distributions, like Linux Mint, Linux Lite, elementary OS, etc.
On the desktop, open the terminal. You can find it in the menu, or use the Ctrl+Alt+T keyboard shortcut. If you are logged on to an Ubuntu server, you already have access to a terminal.
In the terminal, you just have to use the following command:
sudo apt update && sudo apt upgrade -y
It will ask for a password. You can use your account’s password. You won’t see characters on the screen while typing, so keep on typing your password and hit enter. This will update the packages in Ubuntu.
or you can also write those two commands separately, as following.
sudo apt update
sudo apt upgrade
Explanation: sudo apt update
This command updates the local database of available packages. If you don’t run this command, the local database won’t be updated and your system will not know if there are any new versions of packages available.
This is why, when you run the “sudo apt update” command, you’ll see lots of URLs in the output. The command fetches the package information from the respective repositories (the URLs you see in the output).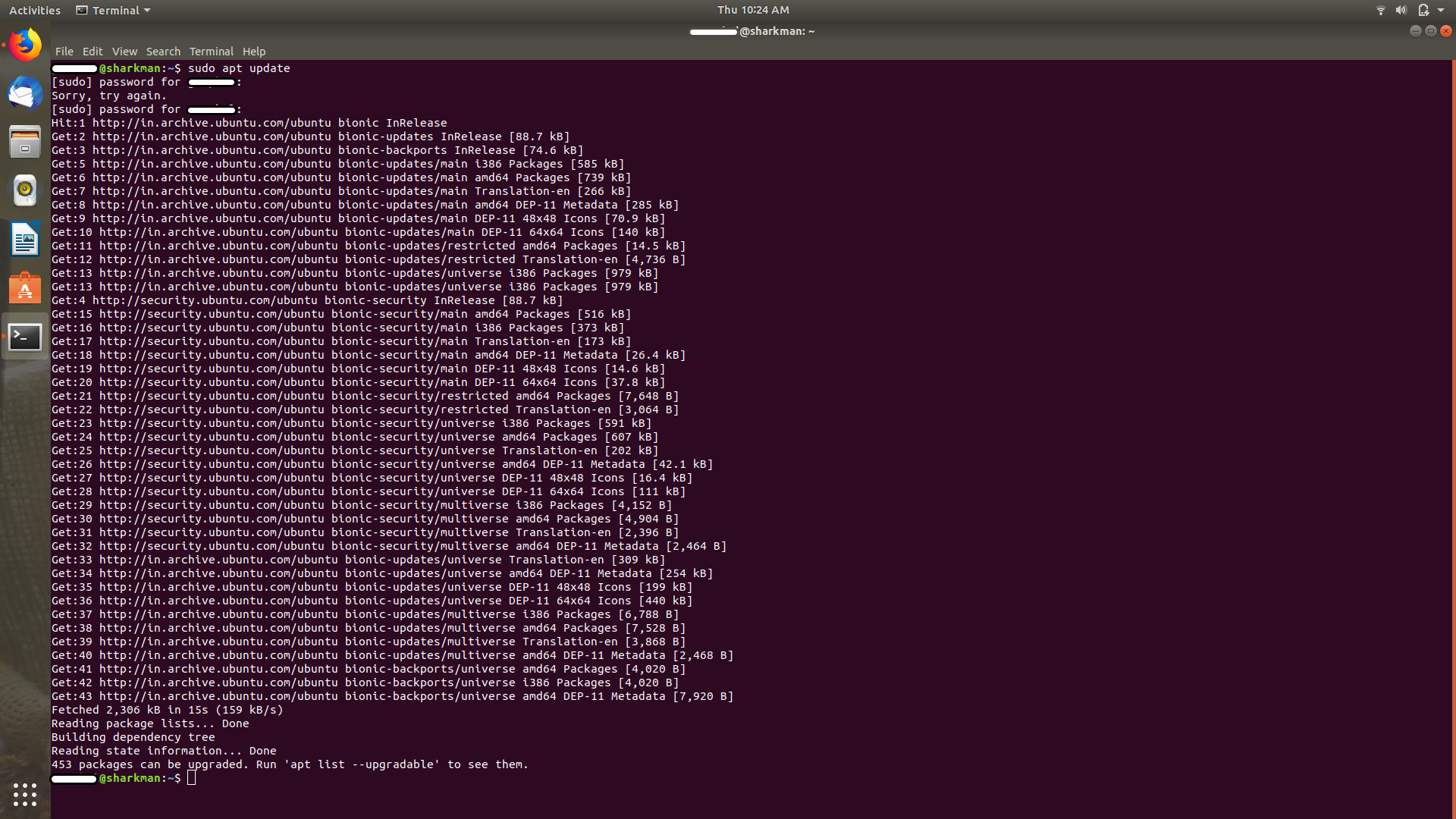
At the end of the command, it tells you how many packages can be upgraded. You can see these packages by running the following command:
apt list --upgradable
Explanation: sudo apt upgrade
This command matches the versions of installed packages with the local database. It collects all of them, and then it will list those packages that have a newer version available. At this point, it will ask if you want to upgrade the installed packages to the newer version.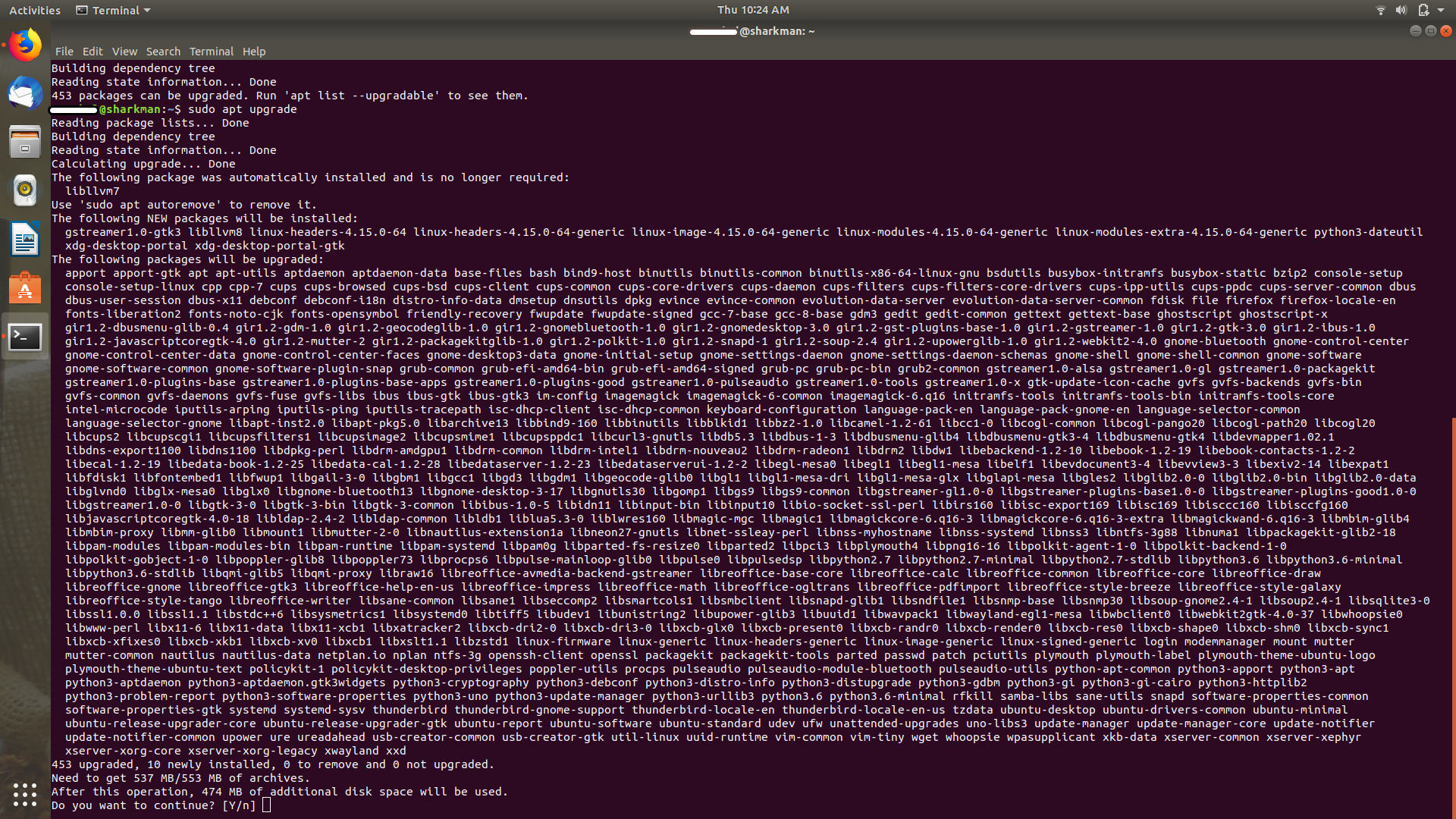
You can type “yes,” or “y,” or just press enter to confirm the installation of updates.
So the bottom line is that “sudo apt update” checks for the availability of new package versions, while “sudo apt upgrade” actually installs the new versions.
The term update might be confusing, as you might expect the “apt update” command to update the system by installing new software, but that’s not how it works.
Method 2: Update Ubuntu via the GUI [For Desktop Users]
If you are using Ubuntu as a desktop, you don’t have to go to the terminal to update the system. You can still use the command line, but it’s optional for you.
In the menu, look for “Software Updater” and run it.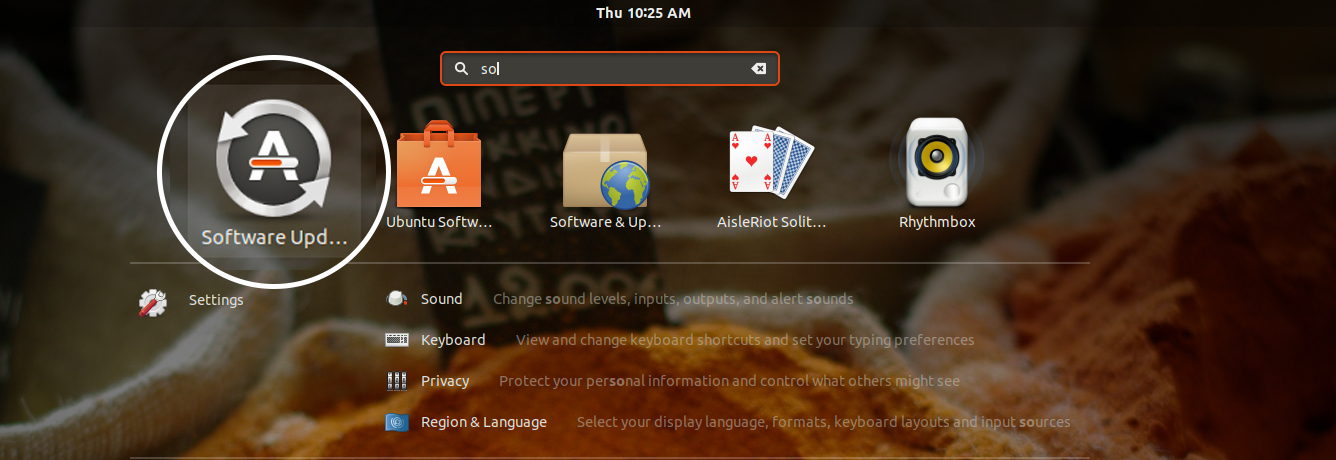
It will check if there are updates available for your system.

If there are updates available, it will give you the option to install the updates. 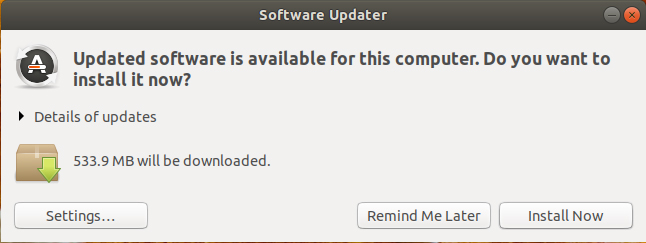
Click on “Install Now.” It may ask for your password.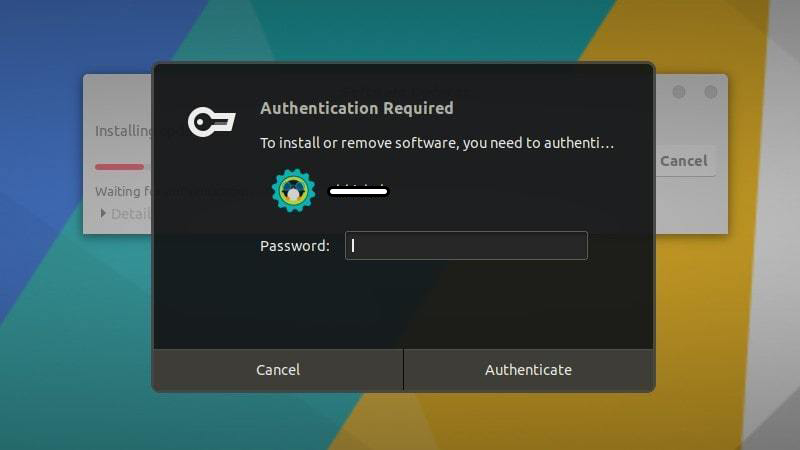
Once you enter your password, it will start installing the updates.

In some cases, you may need to reboot your Ubuntu system for the installed updates to work properly. You’ll be notified at the end of the update if you need to restart the system.

You can choose to restart later if you don’t want to reboot your system straightaway.

Tip: If the software updater returns an error, you should use the command “sudo apt update” in the terminal. The last few lines of the output will contain the actual error message. You can then search on the internet for that error and fix the problem.
A few things to keep in mind about updating Ubuntu
You just learned how to update your Ubuntu system. If you are interested, you should also know these few things relating to Ubuntu updates.
Cleaning up after an update
After an update, your system may have some unnecessary packages that are no longer required. You can remove such packages and free up some space by using this command:
sudo apt autoremove
In the case of Linux kernel updates, you’ll have to restart the system after the update. This can be a problem if you don’t want downtime for your server.
Ubuntu version upgrades are different from package upgrades
The update methods discussed here keep your Ubuntu install fresh and updated. It doesn’t cover OS version upgrades (for example, upgrading Ubuntu 16.04 to 18.04).
Ubuntu version upgrades are an entirely different thing. They involve updating the entire operating system core. You’ll need to make proper backups before starting this lengthy process.



0 Comments