Importance of data backup and recovery in Windows
Backup refers to a process of creating and storing copies of data that can be used to protect organizations against data loss or damage. Recovery refers to restoring the data from the backup to the original location, or to an alternate location where it can be used in place of the lost or damaged data.
Backup is a solution to prevent primary data failures which can be the result of hardware or software failure, data corruption, or a human-caused event, such as a malicious attack (virus or malware), or accidental deletion of data.
Two types of backups are :
- Online/Cloud based : Online backups are those backups which rely on a cloud server which is accessible with availability of the internet. Your data is stored in the cloud servers of companies which also ensures your data privacy and security. Some common examples include Google drive, Dropbox, icloud, onedrive and etc.
- Offline backups : Offline backups refers to those backup mediums which doesn’t require internet connection to store and retrieve your data. These are physical storage devices which contain a specific storage capacity to backup your personal or professional data. Some common examples include usb flash/pen drives, external hard drives, network attached storage devices.
Backup and restore a PC
- Select the Start button, then select Control Panel > System and Maintenance > Backup and Restore.
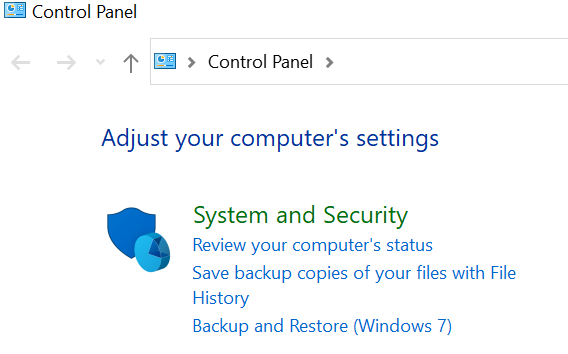
- Do one of the following:
- If you’ve never used Windows Backup before, or recently upgraded your version of Windows, select Set up backup, and then follow the steps in the wizard.
- If you’ve created a backup before, you can wait for your regularly scheduled backup to occur, or you can manually create a new backup by selecting Back up now.
- If you’ve created a backup before, but want to make a new, full backup rather than updating the old one, select Create new, full backup, and then follow the steps in the wizard.
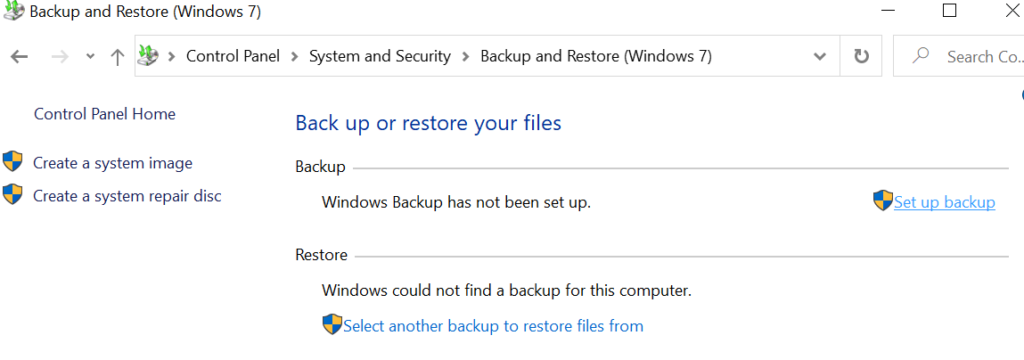
Recovery of the files :
- Right-click the Start button, then select Control Panel > System and Maintenance > Backup and Restore.
- Do one of the following:
- To restore your files, choose Restore my files.
- To restore the files of all users, choose Restore all users’ files.
- Do one of the following:
- To look through the contents of the backup, select Browse for files or Browse for folders. When you’re browsing for folders, you won’t be able to see the individual files in a folder. To view individual files, use the Browse for files option.
- To search the contents of the backup, select Search, type all or part of a file name, and then select Search.
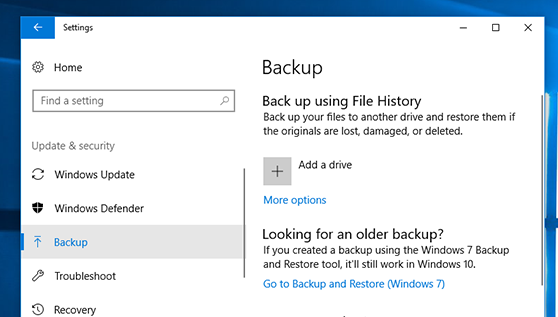
For window 10 users:
- Type backup settings and select on backup in the left icon under Windows Security and add a drive where you want to keep your backup.
Restore your files with File History :
- If you’re missing an important file or folder that you’ve backed up, here’s how to get it back:
- In the search box on the taskbar, type restore files, and then select Restore your files with File History.
- Look for the file you need, then use the arrows to see all its versions.
- When you find the version you want, select Restore to save it in its original location. To save it in a different place, right-click Restore, select Restore to, and then choose a new location.

0 Comments